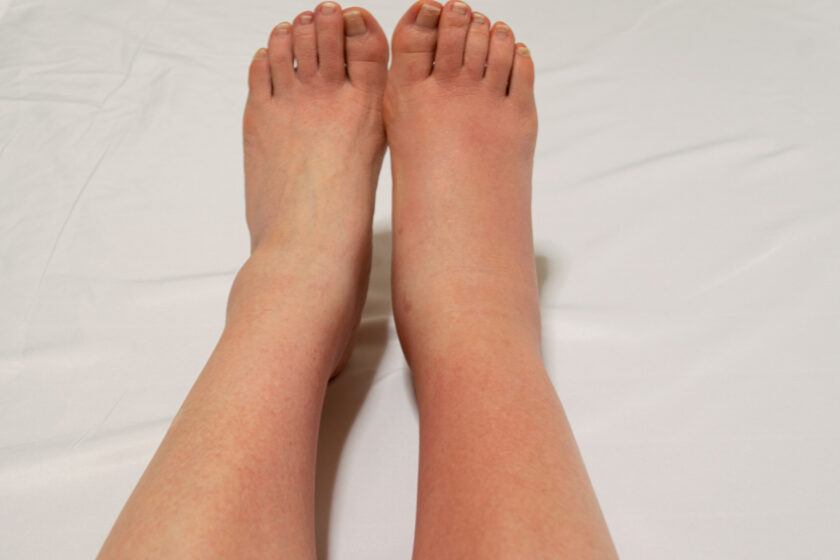
Swollen legs: Don’t Ignore Them, Understand Them
As we navigate through life’s twists and turns, our legs bear the brunt of our journeys—quite literally. Yet, when swelling in the legs arises, it’s more than a mere inconvenience; it’s a signal, a whisper from our body, hinting at underlying complexities.
From the aftermath of leg injuries to the transformative journey of pregnancy, swollen legs paint a portrait of our health’s narrative.
Join us as we delve into the myriad causes of swollen legs, from the intricate procedures of varicose vein surgery to the simplicity of finding a vascular surgeon nearby, seeking to understand and alleviate this common yet significant discomfort.
Impact of Varicose Veins on Leg Health and Overall Well-Being
Varicose veins, stemming from factors like leg injuries or pregnancy, significantly affect leg health and overall well-being. Swelling in the legs, a hallmark symptom can lead to discomfort and potential complications.
Treatment options such as varicose vein surgery or sclerotherapy are vital for managing symptoms. Consulting a vascular surgeon nearby ensures tailored care, addressing swollen legs’ root causes effectively.
With proper treatment, individuals can experience relief from discomfort, improved leg health, and enhanced overall well-being.
Risk Factors for Varicose Veins
Understanding the risk factors associated with varicose veins is essential for prevention, early detection, and appropriate management.
Prolonged Standing:
Prolonged standing is a well-established risk factor for varicose veins, as it increases pressure within the veins of the lower extremities, impairing venous return and causing blood to pool in the veins.
Occupations that require prolonged periods of standing, such as retail workers, healthcare professionals, teachers, and factory workers, are particularly susceptible to developing varicose veins.
Individuals in these occupations may experience symptoms such as swelling in the legs, heaviness, aching, or cramping, especially after long shifts on their feet.
Obesity:
Obesity is another significant risk factor for varicose veins, as excess weight places additional pressure on the veins of the lower body, impeding blood flow and contributing to venous insufficiency.
Additionally, adipose tissue secretes inflammatory cytokines that can further exacerbate vein inflammation and dysfunction.
The effects of obesity on venous circulation are multifaceted, as increased abdominal pressure can also compress the pelvic veins, leading to venous congestion and the development of varicose veins in the legs.
Pregnancy:
Pregnancy poses a unique set of risk factors for varicose veins, primarily due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume that occur during gestation.
Elevated levels of progesterone relax the walls of the veins, causing them to dilate and become more susceptible to valve dysfunction.
Additionally, the growing uterus exerts pressure on the inferior vena cava, impeding venous return from the lower extremities and contributing to venous congestion. Women who have had multiple pregnancies or a family history of varicose veins are at an increased risk of developing the condition during pregnancy.
Age:
Age is a non-modifiable risk factor for varicose veins, as vein health and elasticity naturally decline with advancing age. The valves within the veins may weaken over time, leading to valve incompetence and venous reflux. As individuals age, the risk of developing varicose veins increases, with prevalence rates peaking in the fifth and sixth decades of life. Aging also exacerbates other risk factors, such as prolonged standing and obesity, further contributing to the development of varicose veins.
Genetics:
Genetics plays a significant role in the development of varicose veins, with family history serving as a strong predictor of individual risk. Hereditary factors can influence the structure and function of the veins, predisposing individuals to valve dysfunction and venous insufficiency. Genetic mutations affecting collagen and elastin production may weaken the vein walls, making them more prone to dilation and incompetence. Individuals with a family history of varicose veins are at an increased risk of developing the condition themselves, highlighting the importance of genetic predisposition in varicose veins.
Identifying Personal Risk Factors
Recognizing individual risk factors for health conditions such as varicose veins is crucial for proactive management and prevention. By understanding the factors that contribute to the development of varicose veins, individuals can take steps to mitigate their risk and maintain optimal leg health.
Self-assessment begins with awareness of common risk factors associated with varicose veins, including prolonged standing, obesity, pregnancy, age, and genetics.
Reflecting on personal habits, lifestyle factors, and family medical history can provide valuable insights into individual susceptibility to varicose veins.
For example, individuals who work in occupations that require prolonged periods of standing or have a family history of varicose veins may be at increased risk and should be particularly vigilant in monitoring their leg health.
Self-assessment also involves paying attention to symptoms and changes in leg appearance or sensation. Swelling in the legs, visible veins, heaviness, aching, or cramping may indicate venous insufficiency and warrant further evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Additionally, individuals should consider lifestyle factors such as physical activity levels, diet, and weight management, as these can influence vein health and overall vascular function.
Strategies for Minimizing Risk Factors Through Lifestyle Changes
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into your daily routine, you can minimize risk factors for varicose veins and promote optimal leg health and overall well-being.
1. Stay Active: Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, promotes healthy blood circulation and helps maintain optimal vein health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for varicose veins, as excess weight places added pressure on the veins in the legs. Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
3. Take Breaks from Prolonged Standing or Sitting: If your job requires long periods of standing or sitting, take regular breaks to stretch your legs and shift positions. Incorporating simple leg exercises, such as calf raises or ankle circles, into your routine can also promote healthy blood flow.
Also read – 7 Ways to Protect Your Legs from Varicose Veins at Work
4. Elevate Your Legs: Elevating your legs above heart level for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce swelling and alleviate discomfort associated with varicose veins. Use pillows or a footstool to support your legs while sitting or lying down.
5. Wear Compression Stockings: Compression stockings exert gentle pressure on the legs, helping to improve circulation and prevent blood from pooling in the veins. Wear compression stockings regularly, especially during periods of prolonged sitting or standing, to reduce the risk of varicose veins.
6. Avoid Tight Clothing: Tight clothing, especially around the waist and legs, can restrict blood flow and exacerbate vein problems. Opt for loose-fitting, comfortable clothing that allows for unrestricted movement and circulation.
7. Practice Good Posture: Poor posture can impede blood flow and contribute to vein problems. Maintain good posture while sitting and standing to promote healthy circulation and reduce strain on the veins in the legs.
8. Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day helps maintain optimal blood volume and promotes healthy blood circulation. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily to stay hydrated.
9. Limit Salt Intake: Excess salt can cause water retention and exacerbate swelling in the legs. Limit your intake of salty foods and opt for fresh, whole foods whenever possible to help reduce fluid retention.
10. Seek Regular Medical Evaluation: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify and address potential risk factors for varicose veins early on. If you have a family history of varicose veins or other risk factors, discuss preventive measures and treatment options with your healthcare provider.
How to find the Best Varicose Vein Doctor near me?
Seeking medical assistance for varicose veins is crucial for the effective diagnosis, treatment, and management of this common vascular condition. Varicose veins can lead to discomfort, swelling, and potential complications if left untreated, emphasizing the importance of consulting a qualified healthcare provider.
To find the best varicose vein doctor near you, start by researching online directories, checking credentials, reading patient reviews, and seeking referrals from trusted sources like your primary care physician or friends.
Consider factors such as experience, communication style, treatment options, and convenience when selecting a varicose vein specialist. Trusting your instincts and choosing a doctor who listens to your concerns and provides personalized care can help ensure optimal outcomes and improved leg health.
FAQs
Swollen legs can be a symptom of varicose veins, but they do not directly cause them. Varicose veins occur when the valves in the veins malfunction, causing blood to pool and the veins to become enlarged and twisted. While swelling may accompany varicose veins, the underlying cause is venous insufficiency rather than the swelling itself.
Individuals with certain risk factors are at higher risk for varicose veins. These include older age, family history of varicose veins, being female, obesity, pregnancy, standing or sitting for long periods, and having a history of blood clots or leg injuries. These factors can contribute to weakened vein walls and impaired valve function, increasing the likelihood of developing varicose veins.
To reduce swelling in the legs due to varicose veins, several lifestyle modifications and treatment options are available. Elevating the legs above heart level, wearing compression stockings, engaging in regular exercise to improve circulation, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding prolonged standing or sitting, and seeking medical treatment such as sclerotherapy or endovenous ablation can all help alleviate swelling and discomfort associated with varicose veins.
Warning signs of varicose veins include visible veins that appear dark purple or blue, bulging or twisted veins that may protrude from the skin’s surface, aching or throbbing pain in the legs, heaviness or fatigue in the legs, itching or burning sensations around the affected veins, and swelling, particularly after prolonged periods of standing or sitting. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment.
In the final stage, severe chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) of varicose veins manifests with intense pain, skin discoloration, thickening, slow-healing ulcers, and risks like superficial thrombophlebitis or deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Immediate medical intervention is vital, often involving advanced treatments like vein stripping or stenting to alleviate symptoms and avert complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding varicose veins and their potential progression to severe chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) underscores the importance of early intervention and proactive management.
Seeking prompt medical attention from a skilled vascular surgeon like Dr. Sumit Kapadia is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications associated with advanced stages of varicose veins.
With Dr. Kapadia’s expertise and dedication to patient care, individuals can trust in comprehensive treatment options tailored to their needs, ensuring relief from symptoms and improved overall vascular health.

MBBS, MS, MRCS, DNB-Fellow
Dr. Sumit Kapadia
Dr. Sumit Kapadia / MR KAPADIA SUMIT a gold-medalist from Baroda Medical College, obtained his general surgical training and senior residency from SSG Hospital, Vadodara.

MBBS, MS, MRCS, DNB-Fellow
Dr. Sumit Kapadia
Dr. Sumit Kapadia / MR KAPADIA SUMIT a gold-medalist from Baroda Medical College, obtained his general surgical training and senior residency from SSG Hospital, Vadodara.



