Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Symptoms, Causes & Effective Treatments
What Is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
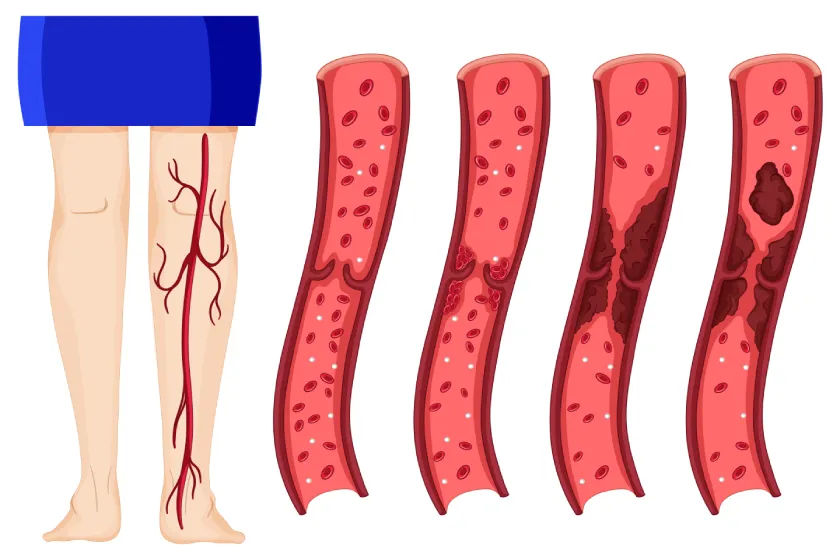
Deep Vein Thrombosis, commonly known as DVT, is a serious vascular condition where a blood clot (thrombus) forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. These clots can partially or completely block blood flow and, if dislodged, may travel to the lungs—causing a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism (PE).
Many patients I see often mistake early symptoms of DVT in the leg for general fatigue or muscle pain. However, identifying early-stage DVT symptoms in the leg can be life-saving. As a vascular surgeon, I urge people to recognize these signs and seek timely consultation.
DVT Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of DVT in the leg early can make a huge difference in outcomes. While some cases may be silent (asymptomatic), common symptoms of DVT in the leg include:
- Sudden Swelling in one leg (rarely both)
- Pain or tenderness in the calf or thigh, especially when walking or standing
- Warmth over the affected area
- Red or discolored skin
- Visible surface veins that may appear larger than usual
Early-stage DVT symptoms in the leg may feel like a muscle cramp or mild discomfort. If left untreated, the condition can escalate quickly.
Causes and Risk Factors of DVT
Understanding the DVT causes is the first step toward prevention and treatment. A DVT typically occurs when the blood flow slows, thickens, and forms a clot. Here are the common causes and risk factors:
Common Causes:
- Injury to a vein, due to surgery or trauma
- Slow blood flow, due to immobility or long travel
- Hypercoagulability, or increased blood clotting (due to certain medical conditions or medications)
Major Risk Factors:
- Recent surgery, especially orthopedic or abdominal
- Long-term bed rest or immobility
- Pregnancy and post-partum phase
- Cancer and chemotherapy
- Family history of blood clots
- Obesity and smoking
- Birth control pills or hormone therapy
If you have one or more of these risk factors, speak to a DVT doctor immediately, especially if you notice any warning symptoms.
DVT vs Varicose Veins
Patients often ask me—“Is DVT the same as varicose veins?” The answer is no.
| Feature | Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) | Varicose Veins |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Blood clot in a deep vein | Weak or damaged vein valves |
| Appearance | No visible change or slight redness | Bulging, twisted, visible veins |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling, warmth, risk of embolism | Aching, heaviness, itching |
| Seriousness | Can be life-threatening | Usually non-life-threatening |
While DVT vs varicose veins may seem similar due to leg pain or heaviness, DVT is far more dangerous and demands urgent medical care. If you have varicose veins, regular vascular assessments can help prevent complications.
Treatment Options for DVT
Once diagnosed, DVT treatment aims to stop the clot from growing, prevent pulmonary embolism, and reduce the risk of recurrence.
1. Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants)
Medications like heparin, warfarin, or newer oral anticoagulants help prevent new clots while the body gradually absorbs the existing ones.
2. Thrombolysis
In severe cases, especially in young patients or when the clot is extensive, clot-dissolving medications may be administered via catheter. Additional newer methods include catheter directed thrombolysis or thrombectomy( removal of thrombus)
3. IVC Filters
For patients who can’t take blood thinners, a filter is placed in the vena cava (large abdominal vein) to catch clots before they reach the lungs.
4. Compression Stockings
Help reduce swelling and lower the risk of post-thrombotic syndrome (long-term leg pain and skin changes).
Early intervention by a DVT doctor or vascular surgeon in India ensures better recovery and fewer long-term complications.
Preventing DVT
DVT can often be prevented with simple changes, especially for those at risk:
- Stay active – Avoid sitting or standing for long hours
- Stretch during travel – Move legs every 2–3 hours during flights or car journeys.
- Stay hydrated – Dehydration thickens blood.
- Maintain healthy weight
- Use compression stockings during long trips.
- Stop smoking
- Follow post-surgical protocols advised by your surgeon.
If you’ve had DVT before or have a family history, consult your vascular specialist regularly.
Conclusion
Deep Vein Thrombosis is not just a leg issue, it’s a silent threat that can escalate into a life-threatening condition if ignored. Recognizing the early-stage DVT symptoms in the leg, understanding the DVT causes, and knowing the difference between DVT vs varicose vein pain can empower you to act quickly.
If you or a loved one is showing signs, don’t wait. I, Dr. Sumit Kapadia, a leading vascular and endovascular surgeon in India, have helped thousands of patients with advanced treatments, early diagnoses, and expert care. When it comes to your veins, trust experience and evidence-backed care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
DVT is a condition where a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the body, most commonly in the legs. It can be dangerous if the clot travels to the lungs, leading to a pulmonary embolism.
The most common causes are immobility, injury to a vein, surgery, or conditions that increase blood clotting, like cancer, obesity, or genetic disorders.
Typical symptoms of DVT in the leg include swelling, pain or tenderness, warmth, and skin discoloration in one leg. Sometimes, it’s mistaken for a muscle cramp.
Blood thinners are the standard treatment. In severe cases, clot removal or thrombolysis may be needed. Early diagnosis and medical supervision are key.



