Noticing a strange swelling, bluish patch, or soft lump on your skin can be worrying, and it often raises questions about what it might mean. These changes may be caused by vascular malformations, which are abnormal formations of blood vessels.
In this blog, we will explore what vascular malformations are, the different types, how they are diagnosed, and the various treatment options available in India.
We will also guide you on how to choose the right treatment, discuss the benefits and risks, and explain when surgery may or may not be necessary.
What is a Vascular Malformation?
Vascular malformation refers to abnormal formations of blood vessels that may involve arteries, veins, capillaries, or lymphatic channels. Unlike normal blood vessels that follow predictable patterns, these vessels grow irregularly and may form clusters, tangles, or enlarged channels. The condition is different from vascular tumors because malformations grow proportionally with the body and do not tend to regress spontaneously.
The symptoms of vascular malformations vary depending on their type, size, and location. Some people may notice visible discoloration or swelling on the skin, while others may experience pain, bleeding, or recurrent infections.
In some cases, malformations affecting internal organs can disrupt blood flow or interfere with organ function. Because vascular malformations are complex, proper diagnosis and management are critical, and early intervention can prevent long-term complications while improving the overall quality of life.
Types of Vascular Malformation
Understanding the type of vascular malformation is the first step in determining the most suitable treatment. There are several recognized types, each with unique characteristics:
Capillary malformations often appear as flat reddish or purplish patches on the skin and are commonly referred to as port-wine stains. They usually do not cause pain, but can darken and thicken over time.
Venous malformations involve abnormal veins that can appear as soft, bluish lumps. These lesions are often compressible, swell with activity, or become more prominent when the affected area is lowered.
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are high-flow lesions in which arteries connect directly to veins, bypassing the capillary network. AVMs can lead to pain, swelling, bleeding, and in some cases, complications such as high-output heart failure if they are large or left untreated.
Lymphatic malformations affect the lymphatic vessels, resulting in fluid-filled cysts or swelling that may be prone to infection. They often appear in the neck, face, or extremities and can cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns.
Combined malformations occur when more than one type of vessel is involved, such as venolymphatic malformations. These are often more complex and require a specialized approach to treatment.
The type of malformation determines which treatment methods are likely to be effective, making proper diagnosis an essential first step.
Get a Proper Diagnosis
Choosing the right treatment for a vascular malformation begins with a thorough and accurate diagnosis. A vascular malformation doctor evaluates the patient through clinical examination and advanced imaging techniques such as Doppler ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans to understand the size, location, and blood flow characteristics of the lesion.
These investigations help distinguish between high-flow and low-flow malformations, which is critical because each type responds differently to treatment.
Vascular malformation centers in India often offer multidisciplinary evaluation, involving vascular surgeons, interventional radiologists, and dermatologists. This team approach ensures that both functional and cosmetic aspects of the malformation are considered, and the best treatment plan is recommended for each patient.
Early and precise diagnosis not only guides treatment but also reduces the risk of complications such as bleeding, pain, or functional impairment.
Treatment Options
Treatment for vascular malformations varies depending on the type, symptoms, and individual patient factors. While some malformations can be safely monitored, others require intervention to prevent complications or improve quality of life.
Observation may be recommended for small, asymptomatic malformations. Regular monitoring ensures that any changes are detected early, allowing intervention if necessary.
Medications can be used to manage pain, inflammation, or swelling associated with certain malformations, although they do not correct the underlying structural issue.
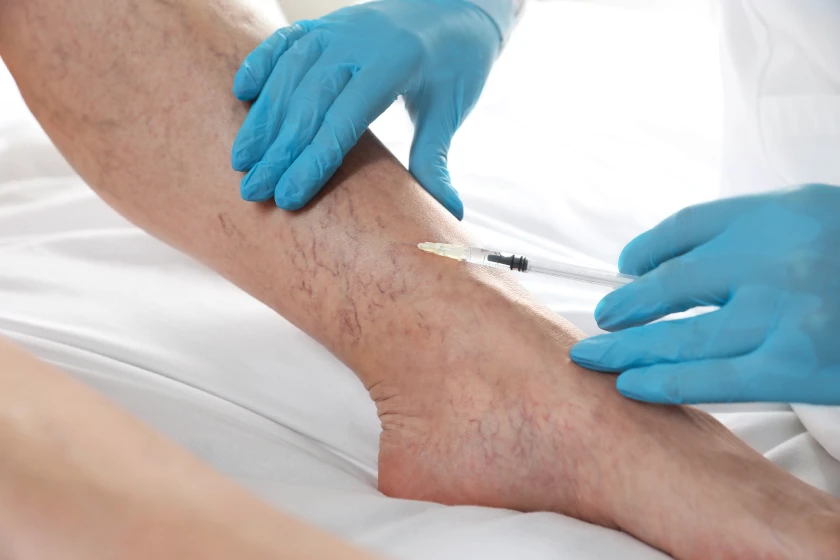
Sclerotherapy is a minimally invasive procedure in which a chemical solution is injected into the malformation to shrink abnormal vessels. This is particularly effective for venous and lymphatic malformations and may require multiple sessions for optimal results.
Laser therapy is commonly used for capillary malformations like port-wine stains. Laser treatment targets the superficial vessels to reduce discoloration and improve appearance, with minimal downtime.
Embolization involves blocking the nidus or abnormal blood vessels, often used for arteriovenous malformations to reduce blood flow before surgery or as a standalone treatment.For embolization, we use glue or onyx commonly, while the use of absolute alcohol is also very effective in complex AV malformations.
Surgery is recommended for large, symptomatic, or complex malformations that cannot be effectively treated with minimally invasive techniques. Surgical excision aims to remove the malformation while preserving surrounding healthy tissue, improving both function and appearance.
A vascular malformation doctor will assess which approach or combination of approaches will provide the best outcome based on the patient’s specific condition.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing Treatment
Before deciding on a treatment plan, several factors should be considered. The severity and symptoms of the malformation play a major role, as pain, bleeding, or swelling often indicate the need for active intervention. The location of the malformation also matters, particularly if it affects vital structures or internal organs, as this may limit certain treatment options.
The type of malformation is equally important because high-flow lesions such as AVMs behave differently from low-flow venous malformations. Potential risks and complications, including scarring, recurrence, and infection, should also be evaluated.
Cosmetic concerns, especially for visible malformations, may influence the choice of laser therapy or minimally invasive procedures. Finally, the patient’s overall health, age, and lifestyle can affect both the safety and effectiveness of the treatment.
Benefits and Risks
Every treatment for vascular malformations comes with potential benefits and risks. Sclerotherapy is minimally invasive and effective for shrinking low-flow malformations, but may require repeated sessions.
Surgery provides definitive results for complex or high-flow lesions but carries risks such as bleeding, infection, or longer recovery. Laser therapy improves appearance with minimal discomfort but is usually limited to superficial lesions.
Understanding the benefits and risks in consultation with an experienced vascular malformation doctor ensures that patients make informed decisions that balance medical safety and personal goals.
Conclusion
Vascular malformations are complex conditions that require careful evaluation and a personalized treatment approach. Some malformations can be monitored or treated with non-surgical options such as sclerotherapy, laser therapy, or embolization, while others may require surgical intervention to achieve optimal results.
Early and accurate diagnosis is essential to prevent complications, improve function, and enhance cosmetic outcomes.
In India, specialized vascular malformation centers provide comprehensive care, combining advanced imaging, interventional techniques, and surgical expertise.
Dr. Sumit Kapadia emphasizes that every treatment plan should be tailored to the individual, addressing both the medical and cosmetic aspects of the malformation. Patients who seek expert care early can prevent progression, reduce discomfort, and achieve the best possible results.
If you notice unusual lumps, discoloration, swelling, or pain, it is essential to consult a vascular malformation doctor promptly. Early diagnosis and proper treatment not only manage the malformation effectively but also improve overall quality of life, allowing patients to lead active, healthy, and confident lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Treatment options include observation, medications, sclerotherapy, laser therapy, embolization, and surgery, depending on the type and severity of the malformation.
Most vascular malformations do not resolve spontaneously and usually require monitoring or active treatment.
A thorough evaluation by a vascular malformation doctor, including imaging and symptom assessment, is necessary to determine the most suitable treatment.
Yes, treatments are generally safe when performed by experienced specialists at a reputable vascular malformation center, though each procedure has specific risks.
Not always. Many malformations respond well to non-surgical options like sclerotherapy, laser therapy, or embolization. Surgery is reserved for large, complex, or symptomatic malformations that cannot be effectively treated otherwise.

Dr. Sumit Kapadia
MBBS, MS, MRCS, DNB-Fellow



